In this practice guideline
Division
This document provides guidelines on the process of the division of a trade mark application as set out in the Trade Marks Act 2002. These guidelines do not constrain the judgement and discretion of the Commissioner of Trade Marks, and each application will be considered on its own merits.
1. Introduction
Section 199(b)(i) of the Trade Marks Act 2002 (“the Act”) allows for the making of regulations to provide for the division of an application for the registration of a trade mark into two or more applications.
Regulations 49-53 of the Trade Marks Regulations 2003 (“the Regulations”) set out the requirements for the division of an application.
2. What is a divisional application
A divisional application is a request to create a new trade mark case by dividing some parts of the original application/registration (parent) into a secondary case (child). The child case retains the priority, application, registration and renewal dates (as applicable, depending on the status of mark at the time of division) of the parent.
An applicant for the registration of a trade mark may apply for division from the application of:
- Part of a series of marks from a series application; 1
- Classes within an application 2
- Specific goods and/or services within an application. 3
3. Why file a divisional application
An applicant may choose to file a divisional application for several reasons including:
- if goods and/or services of an application are in conflict with another trade mark application or registration, the applicant may decide to divide the conflicting goods and/or services into a child application so that the parent application can proceed to acceptance; or
- if some of the goods and/or services of the parent application have been maintained to the point of rejection, the applicant may decide to divide the goods and/or services for which the objection relates into a child application, so that the parent application can proceed to acceptance; or
- if opposition is filed or threatened, the applicant may decide to divide the conflicting goods and/or services to allow the parent application to proceed to registration. Please note, a divisional request in relation to an opposition can only be processed if the opponent agrees that the mark can be divided.
In any of the above cases the applicant may decide to file a divisional application for goods and/or services which are to be divided from the parent application. No time frames for the filing of a divisional apply.
The divisional application will be examined by the examiner of the parent application. The examiner must check that the divisional application meets the criteria for a valid divisional.
4. Filing method for divisional applications
An application for division may be made through the IPONZ online Services - Maintain a Trade Mark - Division/Partial Change of Ownership.
Use of this system also insures that some of the minimum filing requirements as shown below are automatically entered in the Divisional application.
There is no fee for filing an application to divide a trade mark application.
4.1 Minimum filing requirements for divisional application
An application for the division must contain the following information:
-
The name and address of the applicant; 6 and
-
If the applicant has an agent, the agent’s name: 7 and
-
The trade mark application number. 8
-
Where the application is to divide out a mark or marks in a series, the mark or marks to be divided out. 9
-
Where the application is to divide out a class or classes, the list of classes to be divided out. 10
-
Where the application is to divide out some of the goods and/or services, a list of the goods and/or services to be divided out. 11
4.2 Division of accepted marks
A trade mark that has been accepted can be divided if the mark has been opposed.
A division request for an opposed mark can only be processed if the request has been consented to by the opposing party. 12
4.3 Division of registered marks
A trade mark with the status ‘Registered’ or ‘Registered – past expiry date’ may be divided. Regulations 131A to 131C of the Regulations outline the requirements for dividing a registered trade mark, which are largely the same as dividing a trade mark application. A trade mark owner may not file an application for division when the mark has been refused, withdrawn, abandoned or is no longer “active”.
5. Examination
An application for division will be examined to ensure it meets all requirements in the Regulations.
5.1 Application details
The details of the proprietor of the trade mark application must be identical to those of the proprietor of the application for division. An application for division will not be accepted if there is a discrepancy between the proprietor details of the two applications.
The details of the agent of the trade mark application must be identical to those of the agent of the application for division, if any. An application for division will not be accepted if there is a discrepancy between the agent details of the two applications.
5.2 Division of part of a series
An applicant for the registration of a trade mark may apply for division from the application of one or more marks that were the subject of the initial trade mark series application. 13
An application for the division of a series will not be accepted if:
- The original marks did not constitute a series; or
- The application for division is not in respect of the same classes and goods and/or services as in the trade mark application.
An application for the division of a series will not be accepted for all of the marks in the series in the trade mark application. As an application to divide out all of the marks in the series would amount to a re-filing of that application.
5.3 Division of classes
An applicant for the registration of a trade mark may apply for division from the application of one or more of the classes specified in the trade mark application. 14
An application for the division of one or more of the classes will not be accepted where the application for division is not in respect of the same mark or series of marks as in the trade mark application.
An application for the division of a trade mark application will not be accepted for all of the classes in the trade mark application, where those classes include all of the goods and/or services in the initial application. As an application to divide out all of the classes and goods and/or services in the trade mark application would amount to a re-filing of that application.
An application for the division of an application will not be accepted if the class or classes being divided out are not in the specification of the trade mark application, at the time the application for division is filed. Division may only be in respect of the class or classes that remain in the specification at the time the application for division is filed.
5.4 Division of goods and services
An applicant for the registration of a trade mark may apply for division from the application of some of the goods and/or services specified in the trade mark application. 15
An application for the division of some of the goods and/or services will not be accepted where the application for division is not in respect of the same mark or series of marks as in the trade mark application.
An application for the division of a trade mark application will not be accepted for all of the goods and/or services in the trade mark application. As an application to divide out all of the goods and services in the trade mark application would amount to a re-filing of that application.
An application for the division of an application will not be accepted if the goods and/or services being divided out are not in the specification of the trade mark application, at the time the application for division is filed. Division may only be in respect of the goods and/or services that remain in the specification at the time the application for division is filed.
5.5 Striking out goods and services
Where an applicant is given the option of striking out items from a specification to allow the application to proceed to acceptance, they may apply to divide out the non-offending items instead.
However, an application for the division of some of the classes or goods and/or services may not be accepted where there is an outstanding application fee for the class or classes of the items divided out. 16 Regulation 53 prevents an applicant from dividing out goods and/or services or a whole class from a trade mark application and creating a new application without paying a further fee.
An applicant may wish to divide out some goods or services or classes that are the subject of a concern in a Compliance Report so that the application can proceed to acceptance. For example, a trade mark application may be filed in class 25 for “clothing, footwear, headgear and toys”. Where a concern has been raised in a Compliance Report based on “toys” being correctly classified in class 28, the applicant may divide out ”toys” from the application to allow the “clothing, footwear and headgear” goods to proceed to acceptance. However, the application for division in the above example will not be accepted if the applicant has only paid one fee in class 25 and there is an outstanding fee in class 28.
5.6 Amendment
An applicant for division may apply to amend the details in the application for division. The details of an application for division will not be amended where the amendment extends the applicant's rights as prescribed in the initial trade mark application.
6. Division process
Where an application for division is accepted, the trade mark application will be divided. A new application record and number will be created for the divided portion. A fee for the new application record is not required.
The following information will appear in the new application and the initial trade mark application on the IPONZ database:
- on the initial application (parent application) the child application (new application) will appears as a Linked Case under the Activities tab, and the request for Division will also appear as a Linked Case,
- on the new application (child application) “Created from Division of TM” will appear in the History tab, and the parent application will appear as a Linked Case under the Activities tab
Where a mark, class, or any goods or services are divided out of a trade mark application, they will need to be deleted from the initial trade mark application.
If division is requested to allow goods/services unencumbered by objections to proceed to acceptance the request must be made so that the goods/services which do not have objections against them stay with the Original application (parent). The goods/services which have objections against them become the Divisional application (child).
Through the online case management system initiate the division task through Maintain a trade mark – Division/partial assignment.
The task includes the ‘Original Trade Mark’ information and allows division of the application by selecting “Add a new Trade Mark”.
Once selected this adds ‘Divided Trade Mark number 1’ to the task. The specification of ‘Divided Trade Mark number 1’ is a duplicate of the specification of ‘Original Trade Mark’. The specifications of both marks must be edited to ensure that there is no overlap between the goods/services of the Original trade mark and those of the Divided trade mark.
Example:
|
Mark Number |
1010101 |
|
Mark Name |
ELOP’S CHOICE |
|
Goods and services |
Class 28: Toys |
The above was examined and a citation was raised against class 28. The applicant wishes to divide the mark to allow ELOP’S CHOICE in classes 29 and 31 to proceed to acceptance.
As the objection raised related to class 28 it needs to be removed from ‘Original Trade Mark’, which would retain classes 29 and 31:
Original Trade Mark:
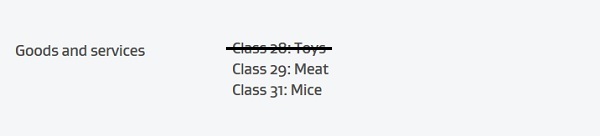
As classes 29 and 31 are covered by the ‘Original Trade Mark’ they need to be removed from ‘Divided Trade Mark number 1’:
Divided Trade Mark number 1:
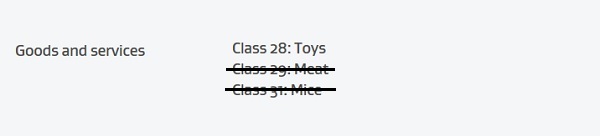
When the divisional request is accepted by the Office ‘Divided Trade Mark number 1’ for class 28 will be issued with an application number and 1010101 ELOP’S CHOICE for classes 29 and 31 will be re-examined prior to acceptance.
6.1 Priority dates
Where an application has been divided, the part of the application that was divided out will be treated as independent from the application from which it derived. However, it will retain the original filing date and convention priority date, if applicable.
An application that has been divided out from another trade mark application will be accorded the same convention priority date as in the initial trade mark application. For a mark with multiple claims to convention priority, the claims to convention priority will apply to each divided application as they applied to the initial trade mark application.
An application that has been divided out from another trade mark application cannot be post-dated.
7. Rejection
Where the details of an application for division are not in order, the application will be rejected.
Where the Commissioner proposes to reject an application for division, the applicant will be sent a Notice of Rejection of Division, advising that the application is rejected. The Notice will state the grounds on which the Commissioner rejects the application to divide the trade mark applications.
Last updated 4 September 2012
Footnotes
- 1 Regulation 49(a) of the Trade Marks regulations 2003.
- 2 Regulation 49(b) of the Trade Marks regulations 2003.
- 3 Regulation 49(c) of the Trade Marks regulations 2003.
- 6 See section 208(3)(a) of the Trade Marks Act 2002.
- 7 See section 208(3)(b) of the Trade Marks Act 2002.
- 8 See section 208(3)(b) of the Trade Marks Act 2002.
- 9 Regulation 51(d) of the Trade Marks Regulations 2003.
- 10 Regulation 51(e) of the Trade Marks Regulations 2003.
- 11 Regulation 51(f) of the Trade Marks Regulations 2003.
- 12 Regulation 51(d) of the Trade Marks Regulations 2003.
- 13 Regulation 49(a) of the Trade Mark Regulations 2003.
- 14 Regulation 49(b) of the Trade Marks Regulations 2003.
- 15 Regulation 49 (c) of the Trade Mark Regulations 2003.
- 16 Regulation 53 of the Trade Marks Regulations 2003.
